How Does a Light Bulb Glow? 💡
A light bulb takes electricity and turns it into light and heat. It’s like a tiny, controlled lightning bolt inside a glass bubble!
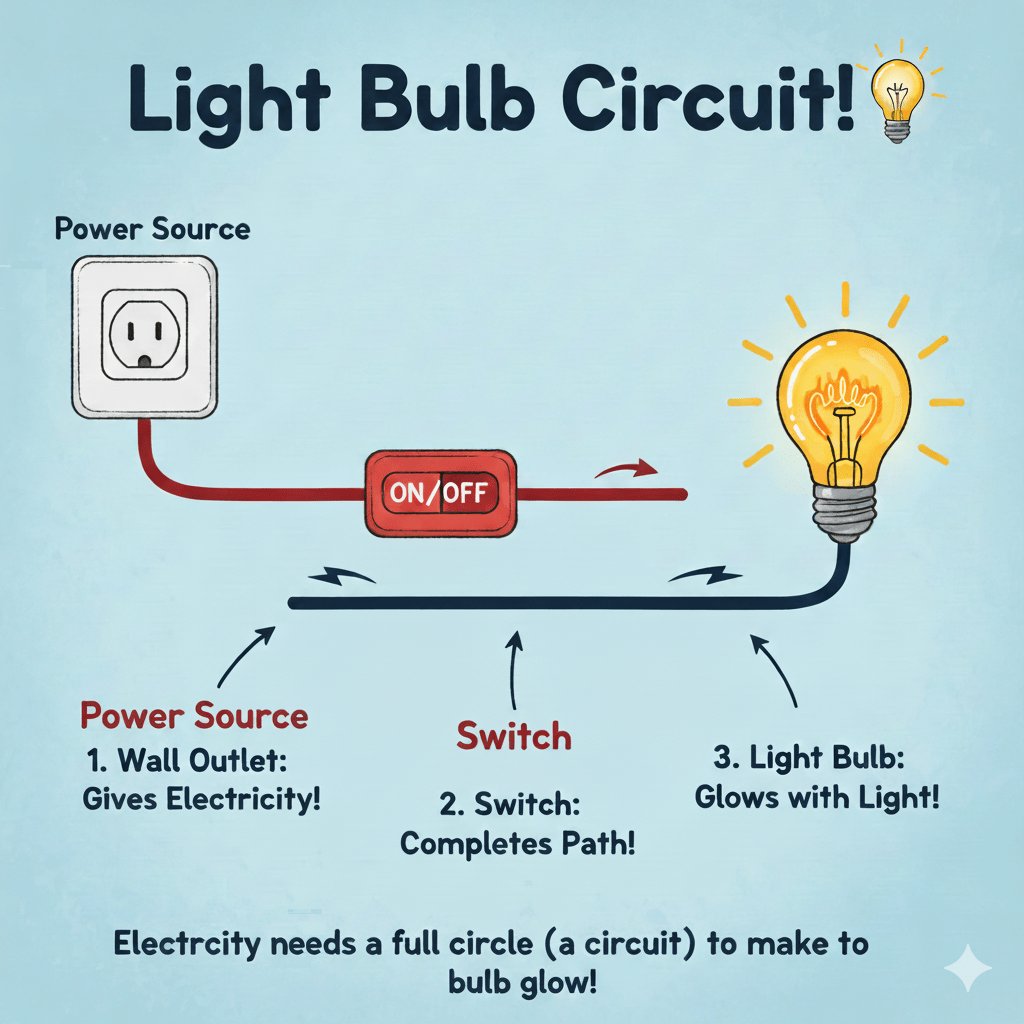
⚡ Step 1: Electricity Moves
Electricity (tiny moving things called electrons) starts from the wall outlet and travels through wires into the light bulb.
👉 It needs a complete circle (called a circuit) to flow.
🌟 Step 2: The Filament
Inside the glass bulb is a very thin, coiled wire called the filament.
- It is usually made of a special metal called tungsten.
- The filament is like the most important part of the light bulb.
🔥 Step 3: Getting Super Hot
When the electricity tries to push through the very thin tungsten filament:
- The filament resists the flow of electricity.
- This resistance makes the filament heat up incredibly fast—like putting the brakes on a moving car, which creates friction and heat!
- It gets so hot (sometimes over $2,000^\circ\text{C}$ or $3,600^\circ\text{F}$!) that it starts to glow bright white or yellow. This is called incandescence.
🛡️ Step 4: No Air Allowed
The glass bulb is not just for protection. Inside, there is no air (oxygen) or it is filled with a safe gas like argon.
- If there was oxygen, the super-hot tungsten would immediately catch on fire and burn up!
- The gas or vacuum keeps the filament safe so it can glow for a long time without burning out.
💡 Simple Science Summary
| Part | Job | Result |
| Electricity | Flows into the bulb | |
| Filament | A thin, coiled wire that resists the flow | Gets extremely hot |
| Glass Bulb/Gas | Protects the hot filament | Keeps the filament from burning up |
| Heat | Causes the filament to glow | Light! |
🧠 Easy to Remember
Electricity + Thin Wire Resistance = Bright Light!
✨ Fun Light Bulb Facts
- The first successful light bulb was made by Thomas Edison.
- The tungsten filament is thinner than a piece of hair!
- Modern light bulbs (like LED and CFL) work differently, using less heat to create light and save electricity.


Leave a comment