Category: Nature
-
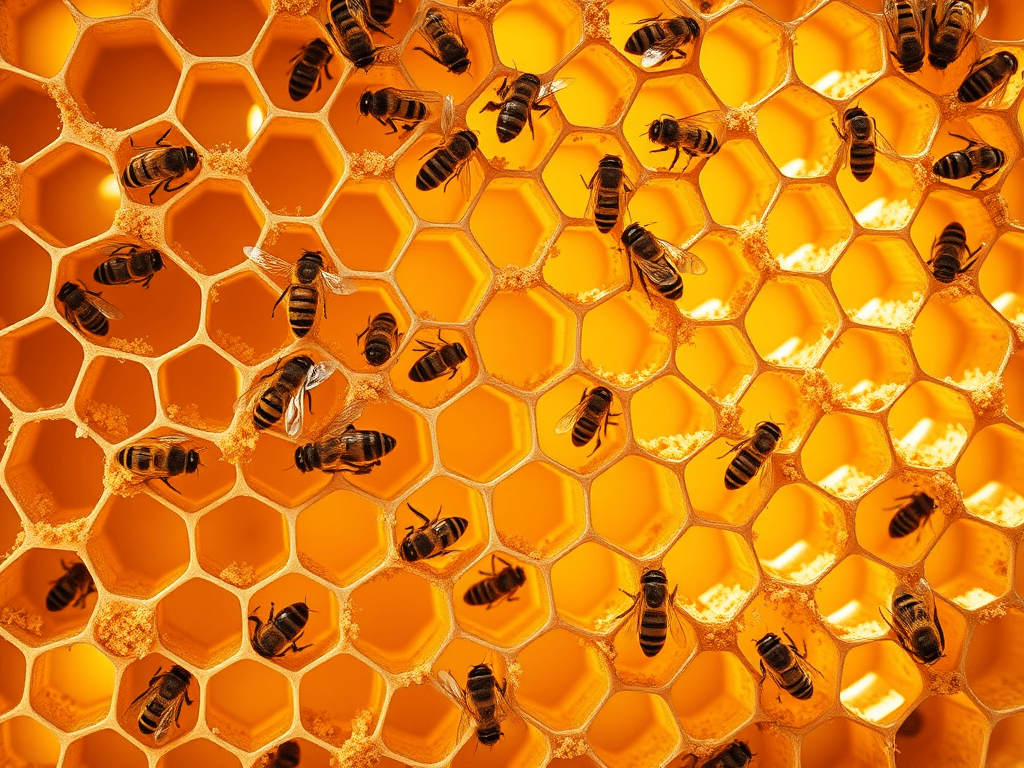

The Science of Honeycomb Hexagons: Nature’s Efficient Design
🍯 Honeycomb Hexagon Science Why hexagons are so strong and efficient 🐝 What is a honeycomb? A honeycomb is the structure bees build to: Each small room is shaped like a hexagon (6 sides). 🔷 Why hexagon shape? 1️⃣ Uses the least material (Very efficient!) 👉 That saves energy for…
-
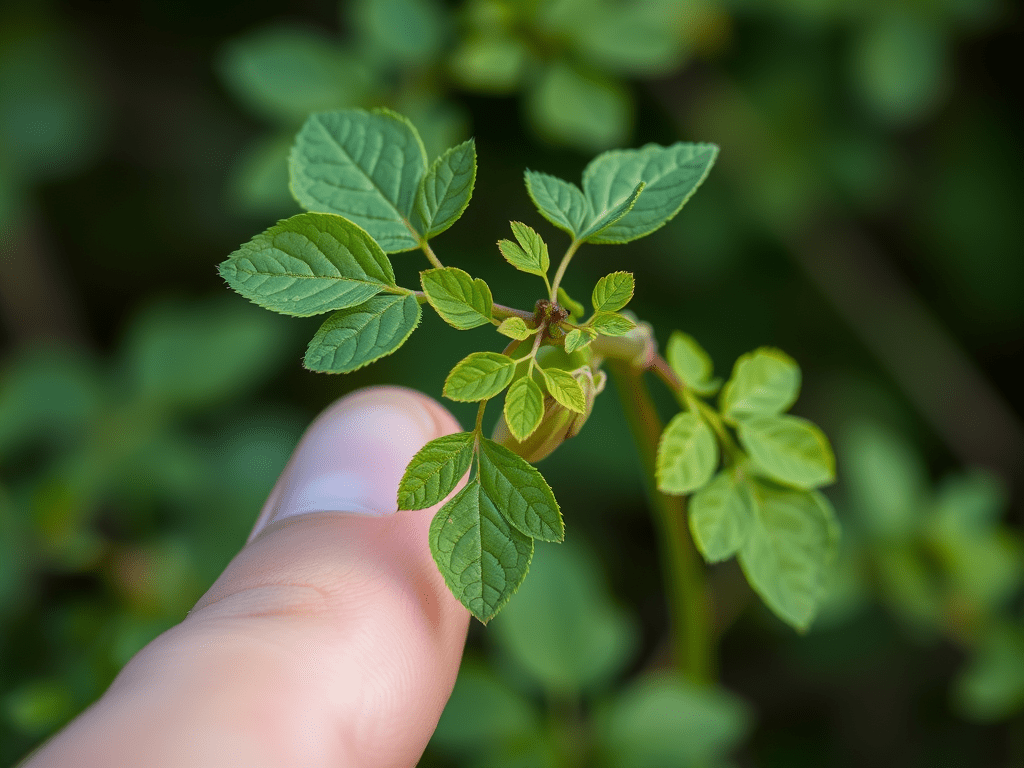

Discover the Fascinating Touch-Me-Not Plant
🌿👉 Touch-Me-Not Plant (Mimosa pudica) – The Science Behind It 🤔 What is the Touch-Me-Not plant? The Touch-Me-Not plant is a small plant whose leaves close and droop when you touch them. Its science name is Mimosa pudica. 👀 What happens when you touch it? It looks like the plant…
-
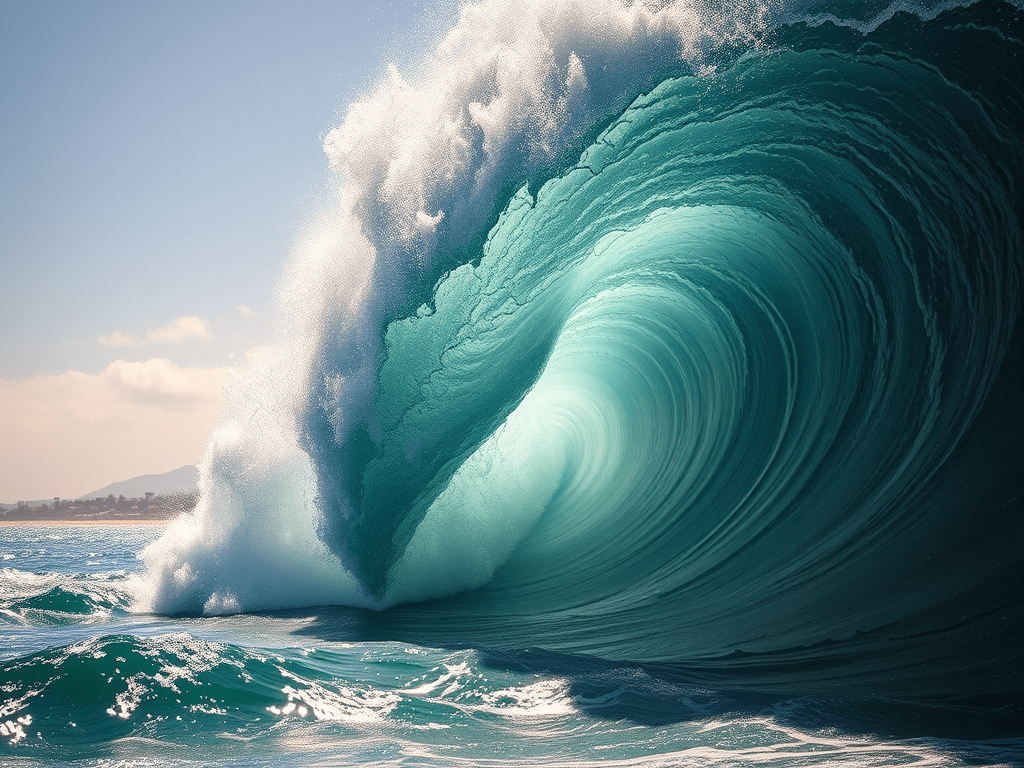

Understanding Tsunamis: Causes and Effects
🤔 What is a tsunami? A tsunami is a series of very large ocean waves caused by a sudden movement under the sea. 👉 It is not a normal wave made by wind. ⚡ What causes a tsunami? Most tsunamis are caused by: 🌊 How does a tsunami form? 1️⃣…
-
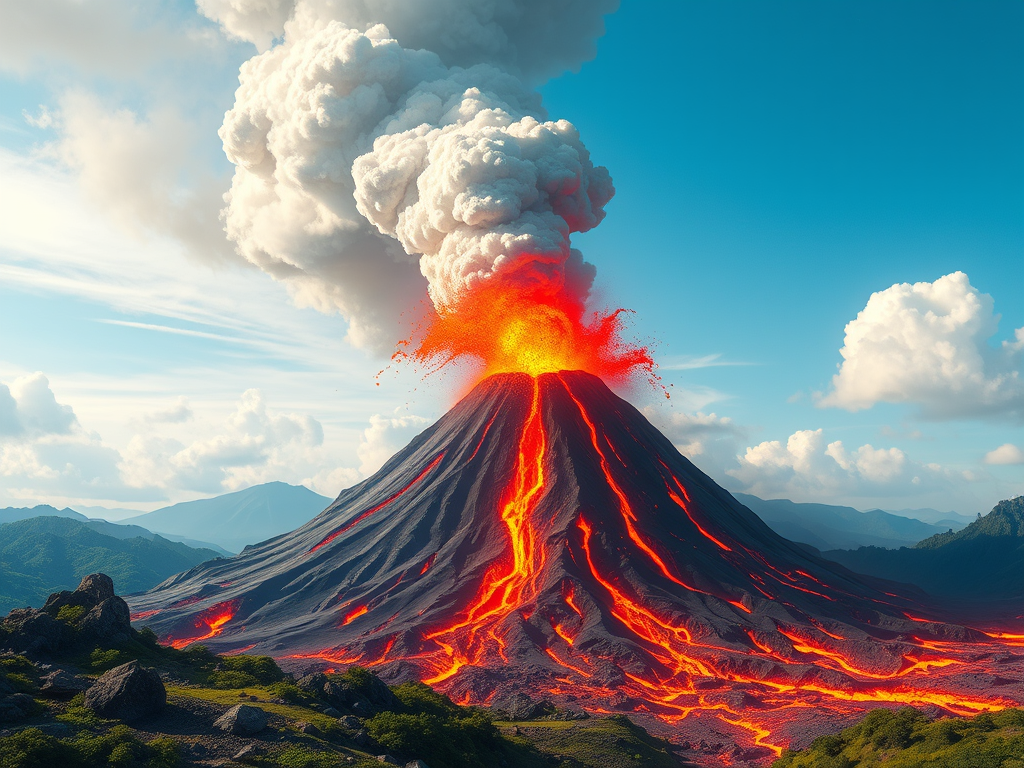

Understanding Volcanoes: Eruption and Structure
🌍 What is a volcano? A volcano is an opening in the Earth where hot melted rock can come out. When a volcano erupts, it releases: 🔥 What is inside the Earth? 🌋 How does a volcano erupt? 1️⃣ Magma builds up under the ground2️⃣ Pressure increases3️⃣ Magma moves up…
-
What You Need to Know About Cyclones
🌪️ What Is a Cyclone? 🌧️ What is a cyclone? A cyclone is a big, powerful storm that forms over warm ocean water. It brings: 🌊 Where do cyclones form? Cyclones form: Different names: 🧠 They are the same kind of storm! 🔄 How does a cyclone form? (Simple steps)…
-
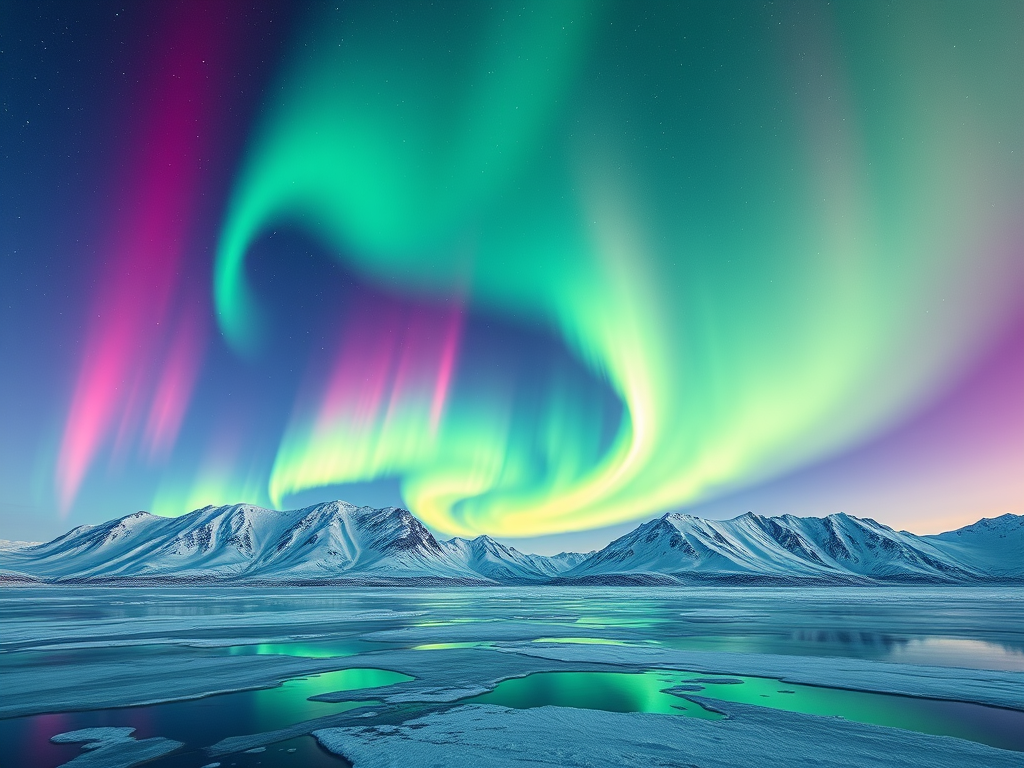

Understanding Auroras: Nature’s Light Show
🌈✨ What Is an Aurora and How Does It Happen? 🌌 What is an Aurora? An aurora is a beautiful natural light show in the sky. 🌍 Different names ☀️ Where do auroras come from? Auroras start at the Sun 🌞 The Sun sends out: 🧲 How Earth helps create…
-
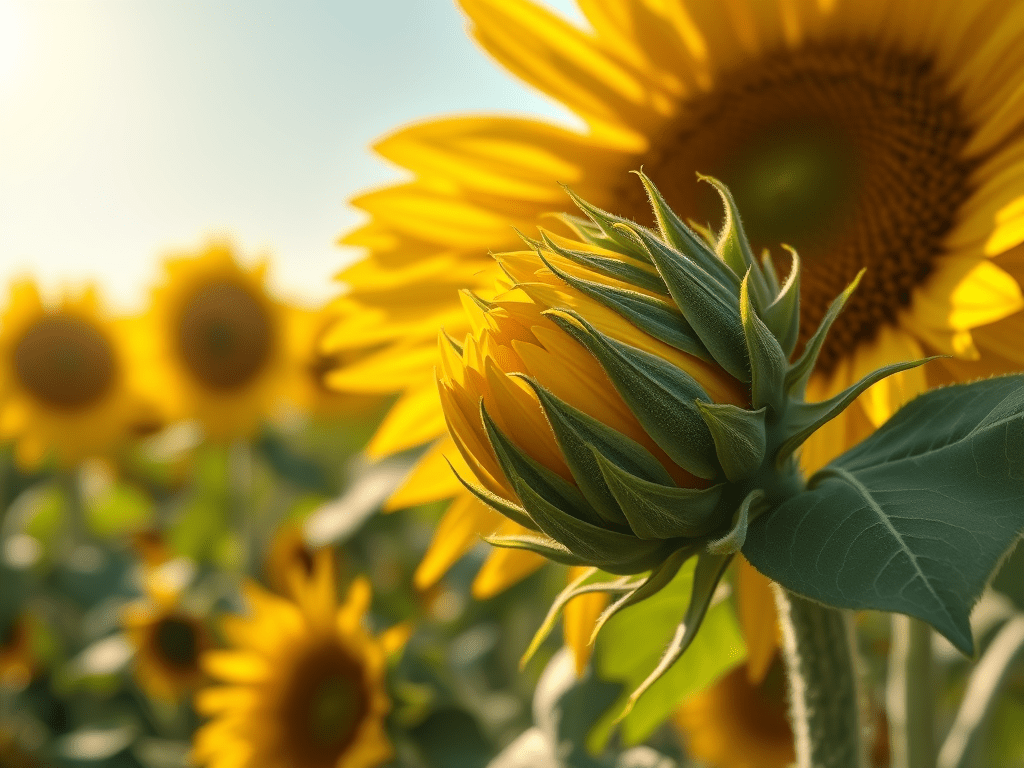

Why Sunflowers Face the Sun
🌻 Why Does a Sunflower Face the Sun? 🌞 What do sunflowers do? Young sunflowers turn their heads to follow the Sun from morning to evening. This movement is called heliotropism(helio = sun, tropism = turning) 🌱 Why do they do this? Sunflowers follow the Sun to: Sunlight helps plants…
-
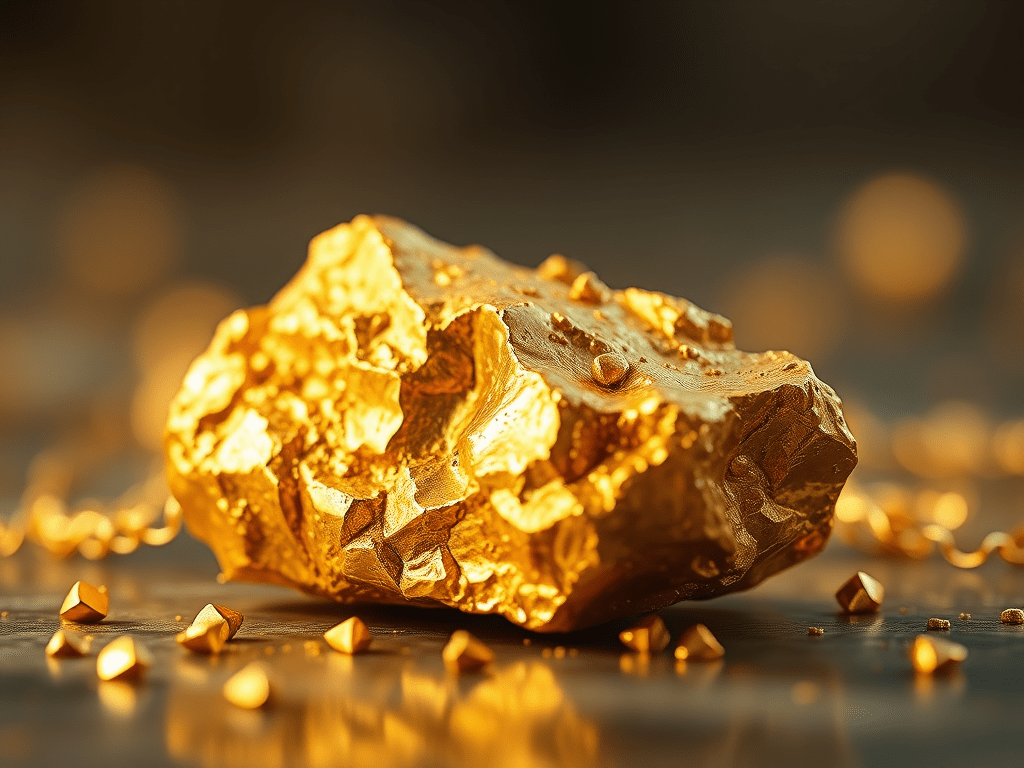

Why Gold is Considered Precious: Top Reasons Explained
💛 Why Is Gold a Precious Metal? ✨ What is gold? Gold is a shiny yellow metal found deep inside the Earth. People have loved gold for thousands of years! 💎 Reasons why gold is precious 1️⃣ Gold is rare 2️⃣ Gold does not rust 3️⃣ Easy to shape 4️⃣…
-

Understanding Carbon: The Building Block of Life
🌱 Carbon – Why It Is Essential for Life (Explained for kids 10+ 😊) 🧪 What is Carbon? Carbon is a very important element (a basic building block of matter). 🧠 If something is alive, it has carbon in it! 🧍 Carbon in Living Things Carbon is part of: 👉…
-
The Fascinating Journey of Earth’s Ancient Water
💧 “The water we drink today is very old” — What does this mean? It sounds strange, but it’s true! Let’s understand it step by step 😊 🌍 Water on Earth is ancient 👉 So the water we drink today is the same water that existed long, long ago. 🔁…
-
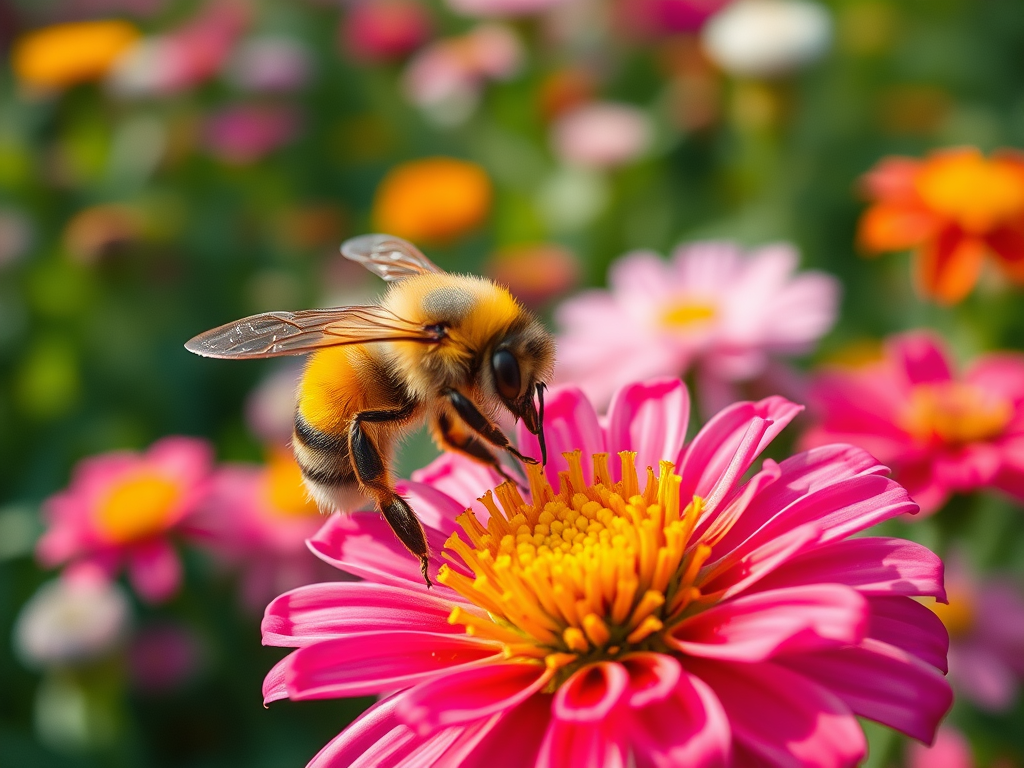

The Importance of Bees for Our Ecosystem
🐝 How Are Bees Special to Earth? 🌼 Bees are nature’s helpers Bees are very special because they help plants grow and food grow. 🌸 1️⃣ Bees help plants make seeds (Pollination) 🧠 Pollination helps plants make: Without bees, many plants could not grow! 🍎 2️⃣ Bees help grow our…
-
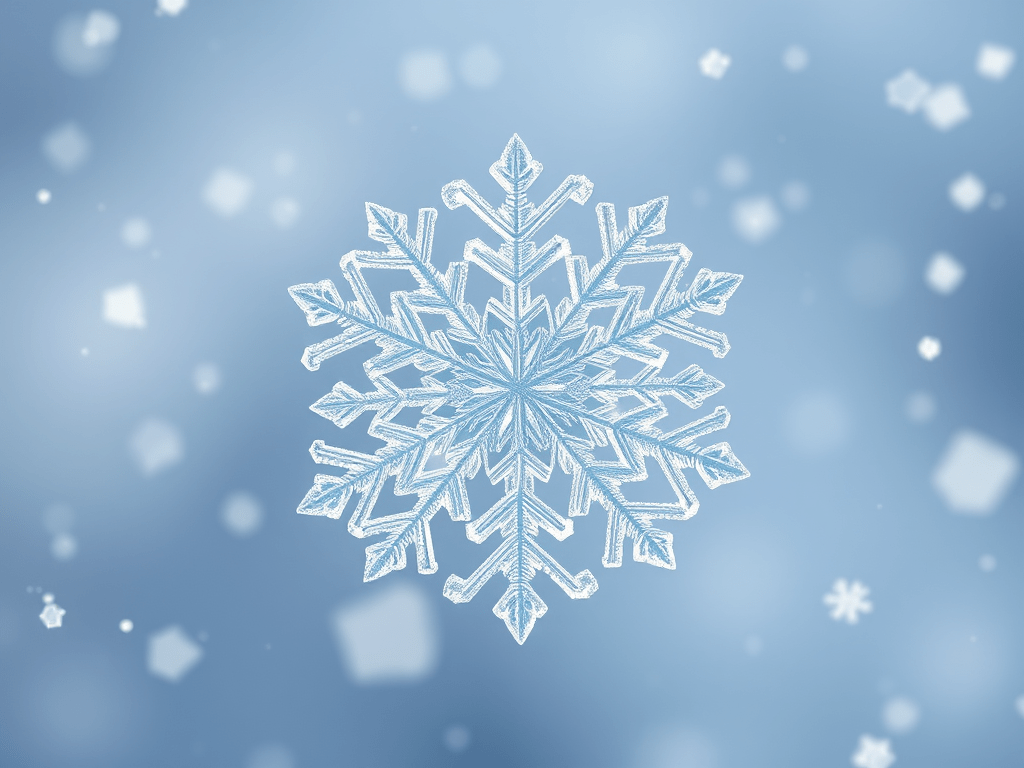

The Science Behind Snowflakes and Snow
❄️ What is Snow? Snow is frozen water that falls from the sky when the air is very cold. 👉 Snow is made of ice crystals, not raindrops. 🌬️ Step 1: Water goes up into the air ☁️ Step 2: Clouds form ❄️ Step 3: Why snow forms instead of…
