-

Understanding Fireflies: Nature’s Glowing Insects
✨ Firefly: The Glowing Insect 🐞 What is a firefly? A firefly is a small insect that can glow in the dark 🌟It is also called a lightning bug (but it’s not a bug—it’s a beetle!). 🔄 Life cycle of a firefly Fireflies have 4 life stages, just like butterflies…
-
The History of Clocks: From Sundials to Modern Timekeeping
⏰ Why Are Clocks Clockwise? And the science behind how clocks were invented 🕒 Why do clocks move clockwise? ☀️ It starts with the Sun! Long ago, people used sundials to tell time. 👉 This shadow direction became the standard direction for timeThat direction is now called clockwise 🔄 🧭…
-

How Ocean Currents Affect Climate and Weather
🌊 What Is an Ocean Current? 🌍 What is an ocean current? An ocean current is like a big river of water moving inside the ocean 🌊➡️It flows in a fixed direction for a long distance. 🤔 Why does ocean water move? Ocean currents move because of: 1️⃣ Wind 💨…
-
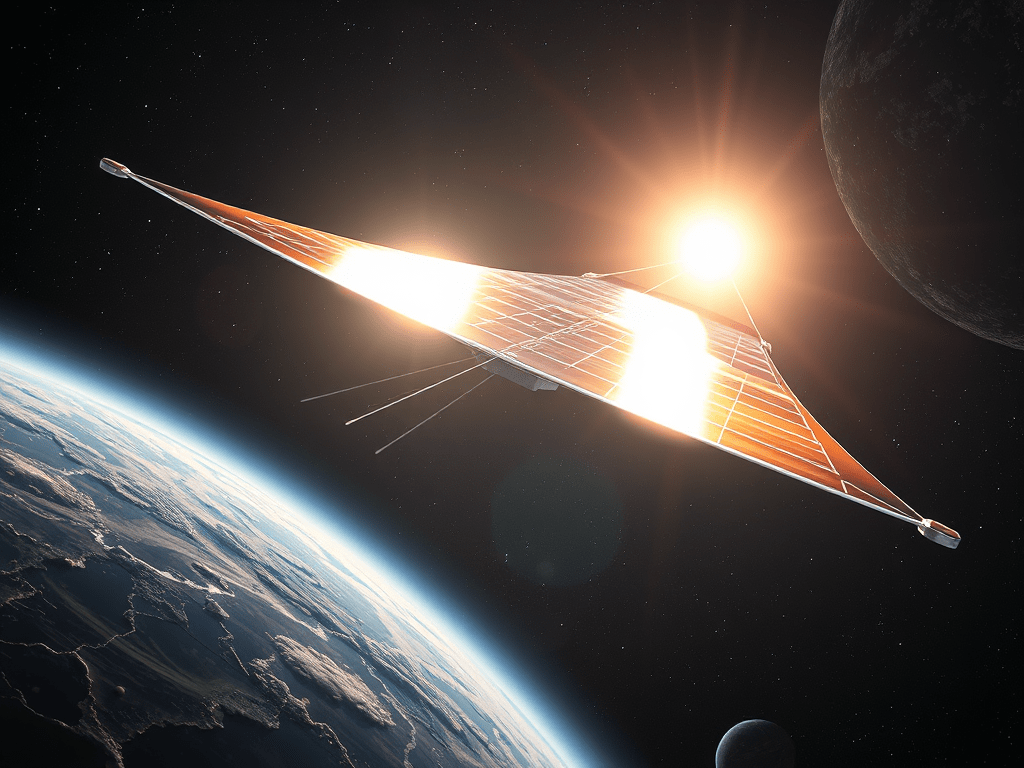
Understanding Solar Sails: How They Propel Spacecraft
☀️⛵ What Is a Solar Sail? 🚀 What is a solar sail? A solar sail is a special kind of space spacecraft that moves using sunlight — not fuel! Just like a boat sail uses wind 🌬️,a solar sail uses light from the Sun 🌞✨ 🌞 How can sunlight push…
-
Can Anything Travel Faster Than Light?
⚡ What Is Faster Than the Speed of Light? 🌟 First, what is the speed of light? So… can anything be faster? 🤔👉 Yes and No! Let’s see how. ❌ Things that are NOT faster than light Nothing physical can travel faster than light ✅ Things that seem faster than…
-
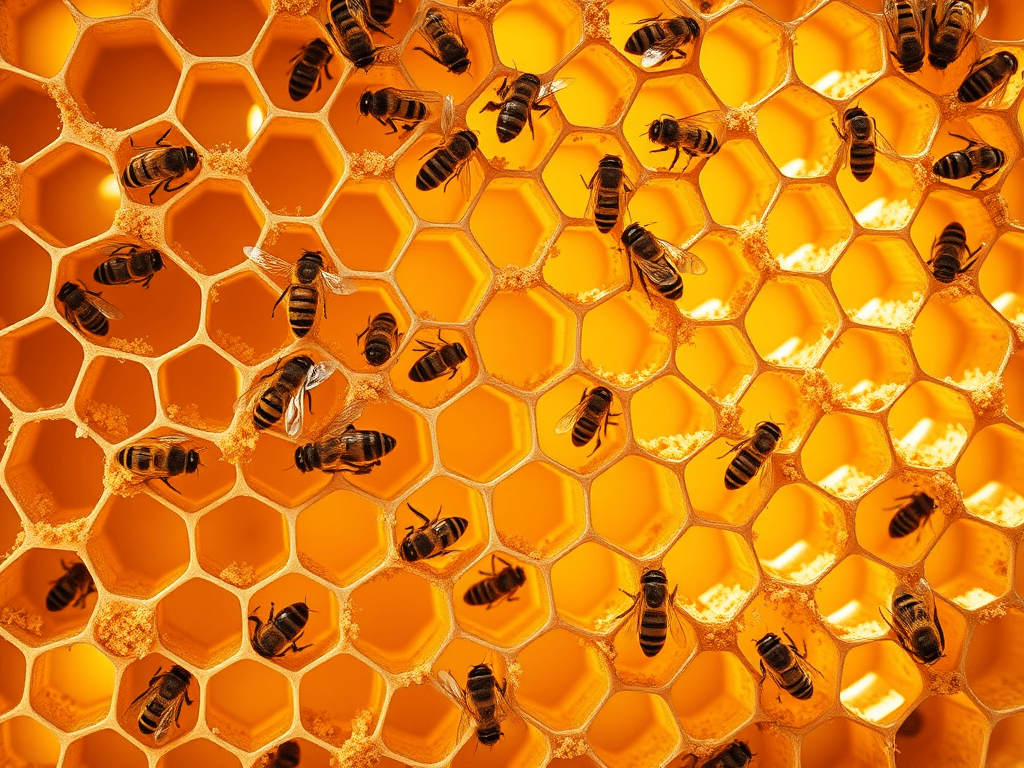

The Science of Honeycomb Hexagons: Nature’s Efficient Design
🍯 Honeycomb Hexagon Science Why hexagons are so strong and efficient 🐝 What is a honeycomb? A honeycomb is the structure bees build to: Each small room is shaped like a hexagon (6 sides). 🔷 Why hexagon shape? 1️⃣ Uses the least material (Very efficient!) 👉 That saves energy for…
-

Understanding Dark Matter vs Dark Energy Explained
🌌 Dark Matter & Dark Energy The universe is full of mysteries, and two of the biggest ones areDark Matter and Dark Energy 🧠✨ They are called “dark” because we can’t see them, but we know they exist! 🌑 What is Dark Matter? 🔍 What it does 👉 Gravity from…
-
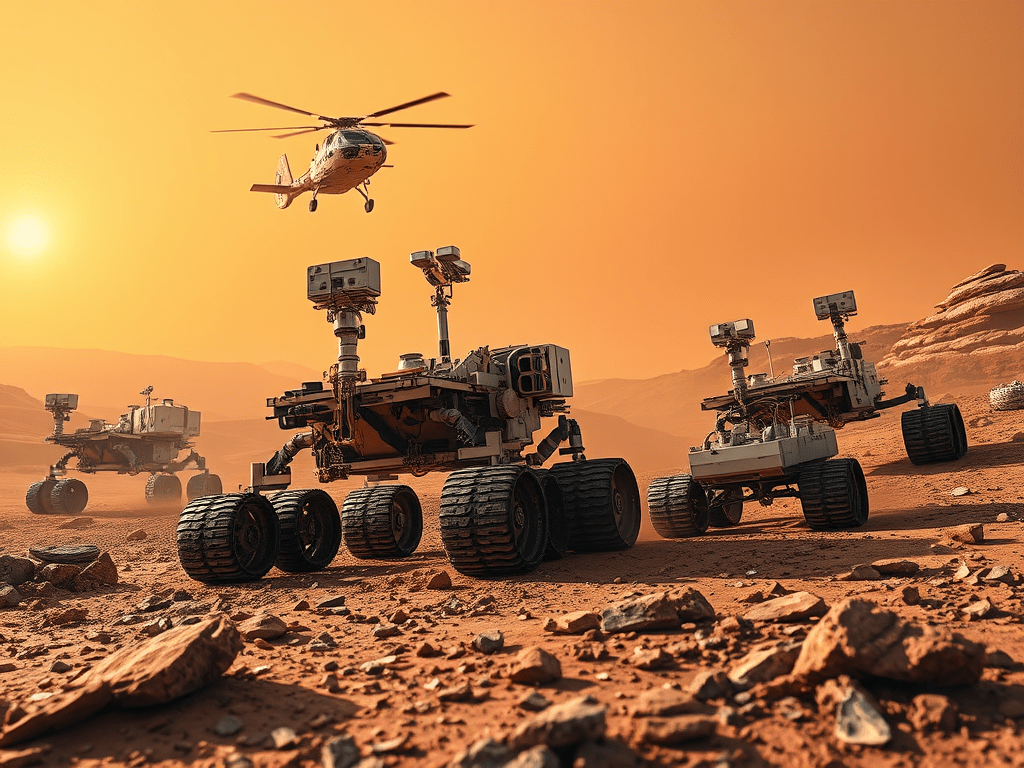
Exploring Mars: The Journey of Robotic Rovers
🤖 Rovers Sent to Mars 🚀 What is a Mars rover? A rover is a robot car 🤖🚗 sent to Mars to: 🟥 Mars Rovers (in order) 1️⃣ Sojourner (1997) 🧠 Fun fact: It worked for 83 days (longer than planned!) 2️⃣ Spirit (2004) 3️⃣ Opportunity (2004) 🌟 Nickname: “The…
-

Why Fire Doesn’t Cast a Shadow: Explained for Kids
🔥 Why Doesn’t Fire Have a Shadow? 🌑 What makes a shadow? A shadow is made when: 👉 Solid objects like a ball or a book make shadows. 🔥 What is fire made of? Fire is not solid.It is made of: So fire is see-through and gives off light. 💡…
-
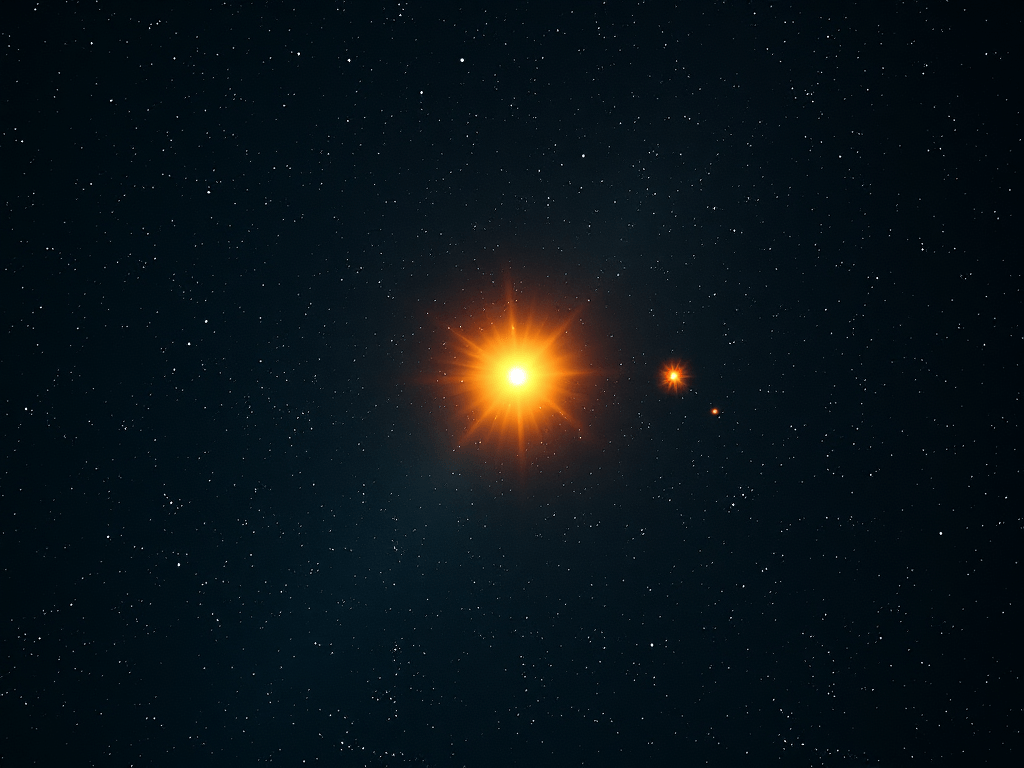
Alpha Centauri: The Three Stars You Should Know
⭐ Alpha Centauri 🌟 What is Alpha Centauri? Alpha Centauri is the closest star system to our Sun 🌞It is not one star — it is three stars together! 🌌 Where is it? ⭐ The three stars in Alpha Centauri 1️⃣ Alpha Centauri A 2️⃣ Alpha Centauri B 3️⃣ Proxima…
-
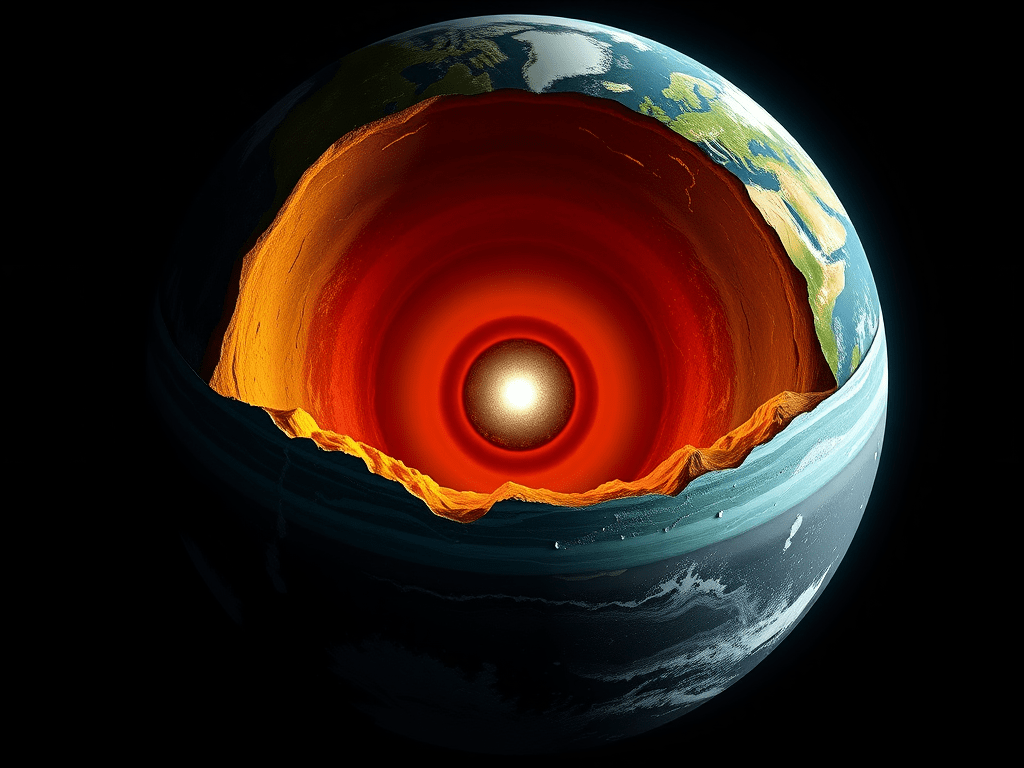
Earth’s Structure: Layers Explained Simply
🌍 Structure of the Earth – Its Layers (Cores) The Earth is made of layers, just like an apple 🍎If we cut the Earth from outside to inside, we see 4 main layers. 🧱 1️⃣ Crust (Outer Layer) 👉 Thickness: Like the apple peel 🪨 2️⃣ Mantle 👉 Causes volcanoes…
-
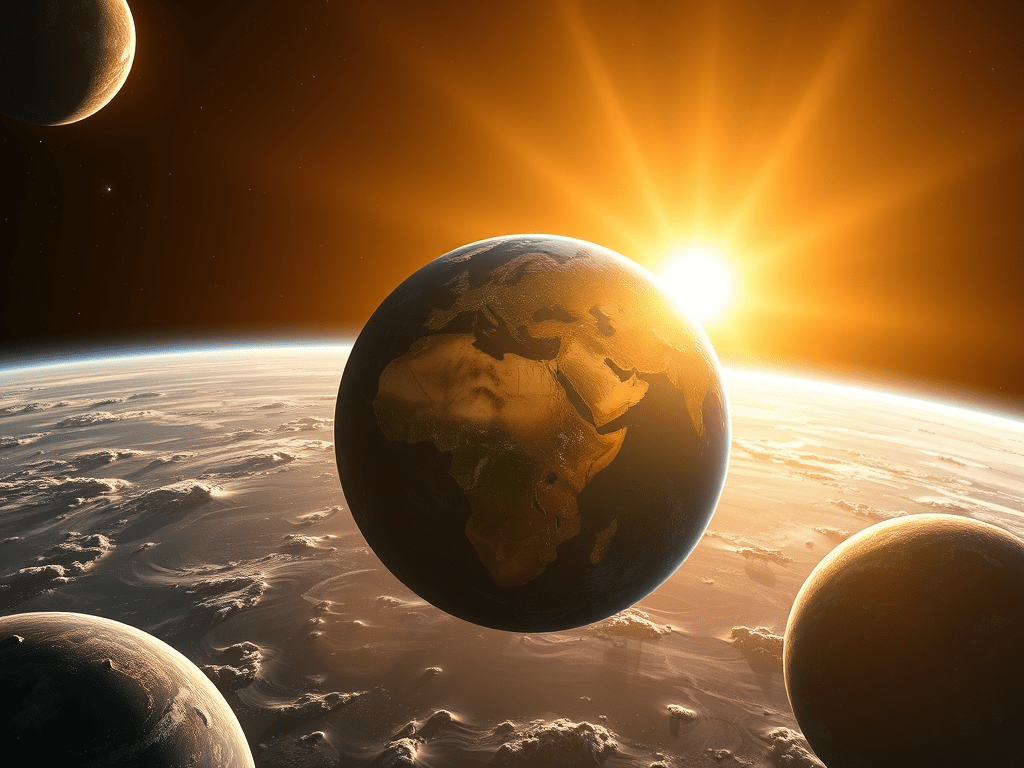
What Defines the Habitable Zone for Planets?
🌍 What Is the Habitable Zone? ☀️ What is the Habitable Zone? The Habitable Zone is a special area around a star where a planet is not too hot and not too cold. 👉 It’s the place where liquid water can exist 💧And water is very important for life! 🔥❄️…
